Contents
- PCB Materials Overview and Market Status
- FR4 Material Details: Performance Parameters and Application Fields
- High-Frequency PCB Materials: Common Types and Selection Standards
- Flexible Substrate Materials: Characteristics, Performance Comparison and Applications
- Main Performance Indicators of PCB Materials
- Practical Guide for PCB Material Selection
- Industry Market Data and Application Trends
- Frequently Asked Questions (People Also Ask)
PCB Materials Overview and Market Status
PCB(Printed Circuit Board) materials mainly include FR-4 (fiberglass substrate), high-frequency substrates, flexible substrates, and aluminum substrates. China’s mainland PCB market accounted for 53.8% of the global proportion in 2020, demonstrating strong market position. High-value-added HDI boards and flexible boards continue to increase year by year.
As a leading PCBA manufacturer in Shenzhen, Mustar specializes in 1-64 layer PCB production, covering FR-4, aluminum substrates, ROGERS and other materials. With 25 years of industry experience, having served customers in 98 countries, the company has accumulated rich experience in PCB material applications and process optimization.
Global and China PCB Material Structure (Based on 2020 data)
Material Type
Market Share (China)
Multilayer boards (4/6 layers)
19.1% / 13.5%
8–16 layer boards
10.4%
HDI boards
16.5%
Flexible boards
17.1%
Rigid & composite boards (single/double-sided)
13.0% / 3.7%
Package substrates
2.7%
High-frequency / High Tg materials
Continuously growing
FR4 Material Details: Performance Parameters and Application Fields
| Material Type | Market Share (China) |
|---|---|
| Multilayer boards (4/6 layers) | 19.1% / 13.5% |
| 8–16 layer boards | 10.4% |
| HDI boards | 16.5% |
| Flexible boards | 17.1% |
| Rigid & composite boards (single/double-sided) | 13.0% / 3.7% |
| Package substrates | 2.7% |
| High-frequency / High Tg materials | Continuously growing |
FR4 material is composed of fiberglass and epoxy resin composite, making it the most universal PCB substrate. Its advantages include high mechanical strength, good insulation, and thermal stability, widely applied in communications, consumer electronics, industrial control, etc. This material has the following typical parameters:
| Key Indicators | Value Range |
|---|---|
| Tensile strength | 200–400MPa, some can reach 600MPa |
| Compressive/Flexural strength | 300MPa~500MPa |
| Elastic modulus | 20–40GPa |
| Dielectric constant Dk | 3.8–4.7 |
| Loss factor Df | 0.02–0.03 |
| Insulator resistivity | >10¹³Ω·cm |
| Dielectric strength | 20–50V/mm |
| Water absorption | Near zero |
| Flame retardant grade | Usually UL94-V0 |
| Application fields | Computers, communications, control |
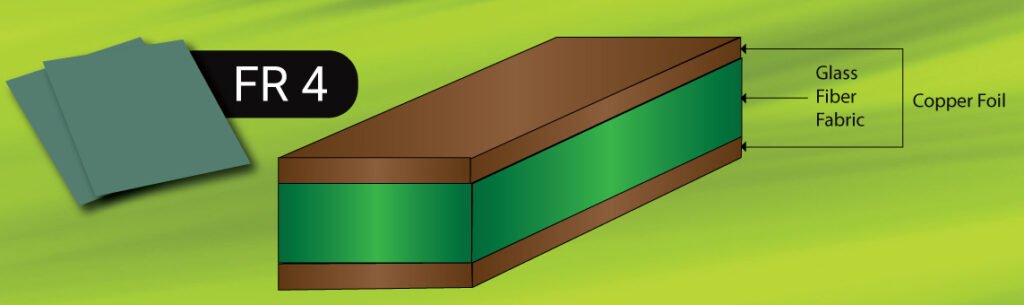
Application Scenarios
FR4 has become the mainstream PCB substrate material due to its comprehensive cost-performance ratio and performance, suitable for most general scenarios. In FR4 material applications, Mustar provides FR4 PCB Assembly solutions with strict IPC-A-610E quality standards and 100% functional testing.
High-Frequency PCB Materials: Common Types and Selection Standards
High-frequency PCBs are used in RF, microwave, 5G, military and other fields. Their core selection parameters include dielectric constant (Dk), loss factor (Df), coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), etc. Common high-frequency materials include PTFE, ceramic-filled polymers, RO4000, polyimide, PPE, etc.
| Material | Dielectric Constant Dk | Loss Tangent Df | Thermal Expansion Coefficient CTE |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE series | 2.2–2.6 | ≤0.001–0.005 | Extremely small |
| Ceramic-filled polymers | 3.5–10+ | 0.002–0.01 | Small to medium |
| RO4000 | 3.38–3.55 | 0.0021–0.0027 | About 40–100ppm/℃ |
Selection recommendations: High-frequency applications need to prioritize low Dk, low Df and excellent dimensional stability. Mustar has professional high-frequency PCB manufacturing capabilities, equipped with ROGERS and other high-frequency materials, providing customized solutions for 5G communications and RF applications.
Flexible Substrate Materials: Characteristics, Performance Comparison and Applications
Flexible substrate commonly used materials are polyimide (PI), polyester (PET), PVA, etc. Their outstanding characteristics are light and thin, bendable, good heat resistance, strong miniaturization adaptation, suitable for mobile phones, wearables, medical and other scenarios.
For more application cases,see PCBA Core Application.
| Material | Temperature Tolerance | Transparency | Mechanical Properties | Application Fields |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | High (above 200℃) | Medium | Excellent (high flexibility/tear resistance) | Mobile phones, medical, aviation |
| PET | Medium | High | Good | Display, consumer electronics |
| PVA | Low | High | Easy processing | Low-end flexible devices |
| Stainless steel | Extremely high | Opaque | Excellent | Special high-temperature applications |

Main Performance Indicators of PCB Materials
- Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): Usually classified as ≥130℃ (low), ≥150℃ (medium), ≥170℃ (high). The higher the Tg, the better the dimensional and thermal stability of the substrate.
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): Linear expansion of materials when heated, the smaller the more stable. High-frequency/high multilayer boards require precise CTE control.
- Dielectric Constant and Loss Factor: Affects signal transmission speed and energy loss. Communication/high-frequency/high-speed boards need to select low Dk, low Df materials.
- Flame Retardancy: UL94-V0 is the mainstream grade.
- Water Absorption and Moisture Resistance: Low water absorption can enhance long-term reliability.
Practical Guide for PCB Material Selection
- Clarify requirements: High-speed signals need high-frequency materials, bending environments need flexible boards, conventional circuits prioritize FR4.
- Combine performance, cost, and manufacturability for comprehensive comparison.
- Pay attention to supply chain and certification requirements (such as RoHS, REACH, UL certification).
With multiple certifications including ISO 9001, IATF 16949, ISO 13485, and 24/7 engineering support services, Mustar provides professional material selection advice for customers. The company has a 500K IC data online query system and 50 professional procurement team members with over 10 years of experience, ensuring supply chain stability.
Industry Market Data and Application Trends
- Global PCB industry concentration is rising, with the top five manufacturers accounting for 23.09% of the market.
- China’s mainland PCB output value accounts for over 53.8% globally, with flexible boards and high-frequency boards developing rapidly.
- The proportion of HDI boards, flexible boards, and IC substrates continues to increase, while traditional single/double-sided boards decline year by year (2020 data).
In high-growth fields such as medical, automotive, and new energy, Mustar has obtained corresponding certifications and established dedicated production lines. The company has 4 SMT lines specifically serving medical and automotive products, ensuring compliance with strict quality standards for industry-specific requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (People Also Ask)
Q1: What are the main differences between FR4, high-frequency boards, and flexible boards?
A: FR4 is the mainstream rigid substrate material with balanced mechanical and electrical properties, suitable for general electronic products. High-frequency boards use special low dielectric polymers, such as PTFE or ceramic-filled resins, with low signal loss, suitable for high-speed communications or RF. Flexible boards use polyimide and other polymer films as substrates, can be bent and rolled, suitable for portable and complex deformation scenarios.
Q2: What are the most important performance indicators when selecting PCB substrates?
A: Main considerations include glass transition temperature Tg, dielectric constant Dk, dielectric loss Df, coefficient of thermal expansion CTE, mechanical strength, water absorption, and flame retardant properties.
Q3: What are the commonly used materials for high-frequency PCBs? What are the selection criteria?
A: Typical materials include PTFE, ceramic-filled polymers, RO4000, LCP, polyimide, etc. Selection should prioritize materials with low Dk, low Df, low thermal expansion, and high dimensional stability.
Q4: What are the most commonly used substrates for flexible boards and their advantages and disadvantages?
A: Mainly uses polyimide (PI), whose advantages are excellent thermal and mechanical properties, can work stably under high bending and high temperature conditions. PET-based boards have high transparency and low cost, but slightly inferior high-temperature resistance, suitable for low-end applications.
Q5: What are the market trends and industry development directions for PCB materials?
A: Industry trends show rapid development of high-density interconnect (HDI), high-frequency high-speed, multifunctional flexible boards, green environmental materials, and specialized application boards (medical, automotive, communications). China is the leader in global PCB capacity and technology advancement.
For more PCB materials application cases and specialized substrate solutions, please visit Mustar (www.pcbamustar.com). As a TOP 1 PCBA manufacturer, we have over 5,000 electronic project experiences, providing one-stop services from PCB manufacturing to component sourcing and PCBA assembly, customizing the best circuit board material selection solutions for you.
We promise prices 10% lower than suppliers of the same quality, 3-7 days rapid prototyping, no minimum order quantity restrictions, helping your products reach the market faster.
Mustar projects: