Quality control in PCBA manufacturing is not just about meeting standards—it’s about building trust with your customers and ensuring long-term success. Moreover, poor PCBA quality can cost manufacturers up to 15% of their total production value through rework, returns, and warranty claims. Therefore, understanding how to ensure PCBA quality becomes crucial for every electronics manufacturer.
Quick Answer: To ensure PCBA quality, manufacturers must implement comprehensive testing methods including visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT), and statistical process control. Additionally, maintaining strict material quality standards and following industry certifications like ISO9001 and IATF16949 are essential.
PCBA Quality Standards: Key Metrics Every Manufacturer Should Track
Understanding quality metrics is the foundation of effective PCBA quality control. Furthermore, these metrics help manufacturers identify problems early and make data-driven improvements. Let’s explore the most important quality indicators that industry leaders track:
Contents
- Essential PCBA Testing Methods for Quality Assurance
- Most Common PCBA Defects and Prevention Strategies
- Advanced Quality Control Technologies in Modern PCBA Manufacturing
- Building a Quality Management System for PCBA Production
- Material Quality Impact on PCBA Reliability
- Industry-Specific Quality Requirements
- Conclusion
| Quality Metric | Industry Benchmark | Description |
|---|---|---|
| First Pass Yield (FPY) | 90-98% | Percentage of PCBAs passing tests on first try |
| Defect Rate | 0.5% – 2% | Percentage of PCBAs with defects after assembly |
| Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | 100,000 hours | Average operational time before failure occurs |
| AOI Detection Rate | 95%+ | Effectiveness in detecting assembly defects |
These metrics serve as benchmarks for how to ensure PCBA quality effectively. For instance, IPC standards provide detailed guidelines for achieving these quality levels. Additionally, companies like Mustar consistently achieve FPY rates above 95% through their rigorous quality control processes.
“Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of intelligent effort.” – John Ruskin
Essential PCBA Testing Methods for Quality Assurance
Implementing the right testing methods is crucial for maintaining high PCBA quality standards. Subsequently, each testing method serves a specific purpose in catching different types of defects. Let’s examine the most effective approaches:
Visual Inspection: Your First Quality Check
Visual inspection remains the most immediate and cost-effective quality control method. In fact, trained operators can identify up to 70% of assembly defects through careful visual examination. Here’s what to look for during visual inspection:
- Solder joint quality: Check for proper wetting, no cold joints, and adequate solder volume
- Component placement: Verify correct orientation, alignment, and positioning
- PCB surface cleanliness: Look for flux residue, contamination, or foreign particles
- Component integrity: Inspect for damaged or missing components
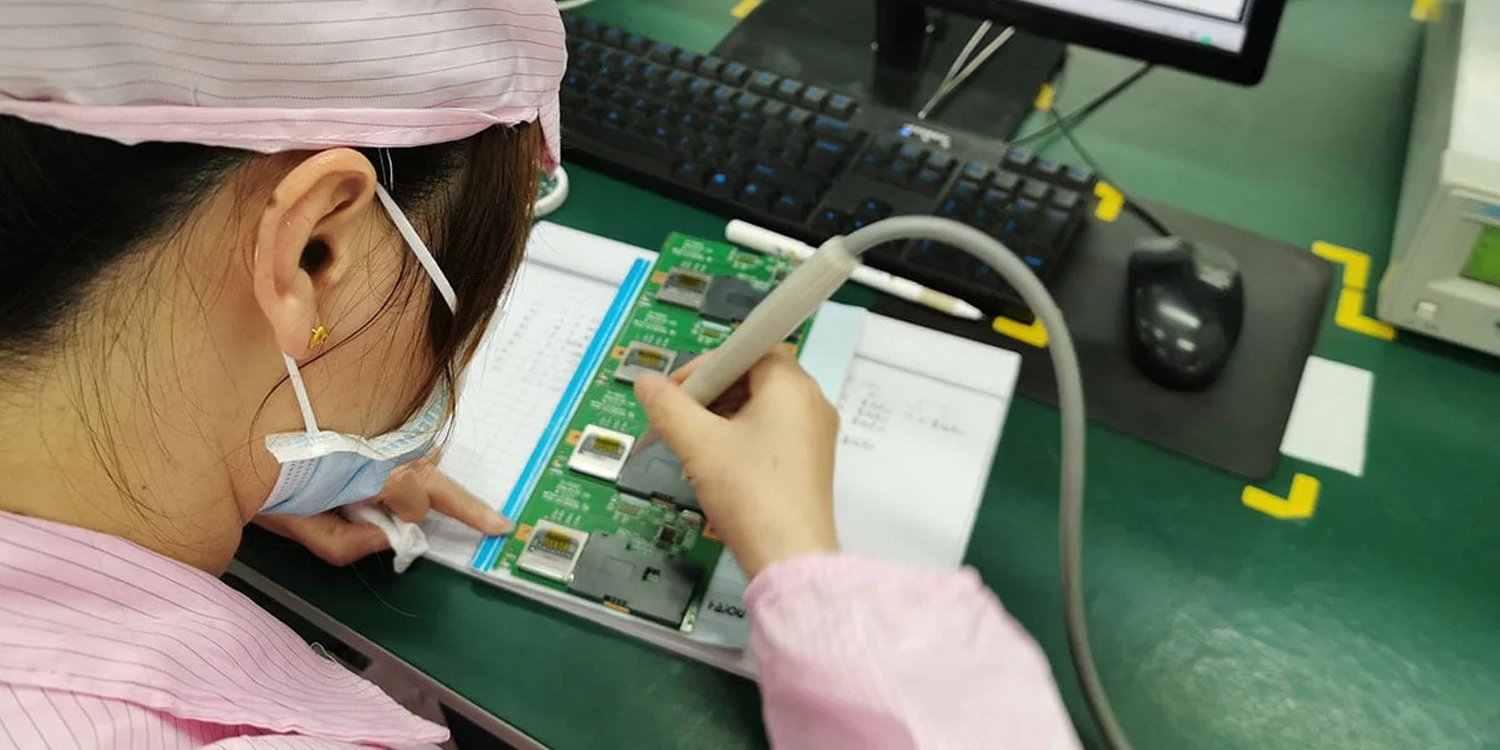 Visual inspection of solder joints and component placement
Visual inspection of solder joints and component placement
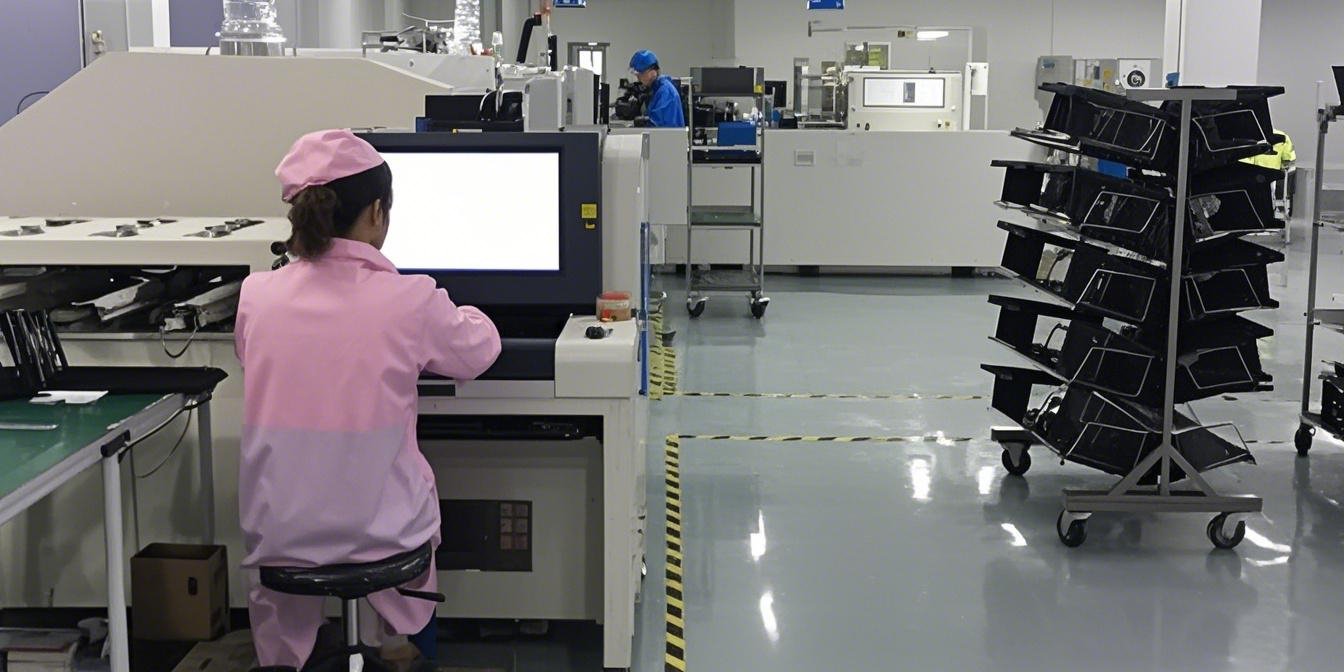 AOI system performing automated quality checks
AOI system performing automated quality checks

X-ray inspection revealing hidden solder defects
Automated Testing Technologies (AOI, SPI, X-Ray)
Automated testing technologies significantly improve both speed and accuracy of quality control. Moreover, these systems can detect defects that human eyes might miss. Here are the key automated testing methods:
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) uses high-resolution cameras and advanced algorithms to detect surface defects. Specifically, AOI systems can identify missing components, incorrect polarity, solder bridges, and insufficient solder. Electronics manufacturing experts recommend AOI for high-volume production lines.
Solder Paste Inspection (SPI) occurs before component placement and ensures proper solder paste volume and placement. Consequently, SPI helps prevent many assembly defects before they occur, improving overall yield rates.
X-ray Inspection is essential for inspecting hidden solder joints, particularly in BGA and QFN components. Furthermore, 3D X-ray systems can detect voids, cracks, and other internal defects that other methods cannot see.
Post-Assembly Testing (ICT, FCT, Functional Testing)
Post-assembly testing ensures that PCBAs function correctly before shipping. Additionally, these tests verify both electrical performance and functional operation:
- In-Circuit Testing (ICT): Tests individual components and circuits for proper values and connections
- Functional Circuit Testing (FCT): Verifies overall circuit functionality under normal operating conditions
- Burn-in Testing: Operates PCBAs under stress conditions to identify early failures
- Boundary Scan Testing: Uses JTAG protocols to test complex digital circuits
Most Common PCBA Defects and Prevention Strategies
Understanding common defects is essential for knowing how to ensure PCBA quality effectively. Moreover, prevention is always more cost-effective than correction. Here are the most frequent PCBA defects and their solutions:
Top 5 PCBA Defects:
- Poor solder joints (cold joints, insufficient solder)
- Component misplacement or wrong orientation
- Solder bridges and short circuits
- Missing or damaged components
- Contamination and flux residue
Prevention Strategies:
First, optimize your soldering temperature profiles using SMT best practices. Subsequently, maintain precise equipment calibration and implement strict process standardization. Additionally, invest in operator training and use high-quality materials from certified suppliers.
Companies like Mustar prevent these defects through their comprehensive quality management system, which includes over 200 stable global suppliers and rigorous incoming material inspection processes.
Advanced Quality Control Technologies in Modern PCBA Manufacturing
Technology continues to revolutionize PCBA quality control methods. Furthermore, these advanced technologies offer unprecedented accuracy and efficiency in defect detection:
AI-Powered Inspection Systems use machine learning algorithms to improve defect detection accuracy over time. Specifically, these systems learn from historical data and can identify subtle patterns that traditional methods might miss.
Boundary Scan Testing (JTAG) allows testing of complex digital circuits without physical test points. Moreover, this technology is particularly valuable for high-density PCBAs where traditional probing is difficult.
EMC/EMI Testing ensures PCBAs meet electromagnetic compatibility requirements. Additionally, early EMC testing prevents costly redesigns and regulatory compliance issues.
Building a Quality Management System for PCBA Production
A robust quality management system forms the backbone of consistent PCBA quality. Moreover, systematic approaches ensure continuous improvement and long-term success. Here’s how to build an effective system:
Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitors key manufacturing parameters in real-time. Consequently, SPC helps identify trends that could lead to defects, allowing corrective actions before problems occur. American Society for Quality provides excellent resources for implementing SPC systems.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) systematically investigates quality issues to identify underlying causes. Furthermore, RCA prevents recurring problems by addressing root causes rather than symptoms.
Continuous Improvement Methodologies:
- Lean Six Sigma for waste reduction and process optimization
- Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycles for systematic improvement
- Regular quality audits and management reviews
- Employee training and certification programs
Material Quality Impact on PCBA Reliability
Material quality directly affects PCBA performance and longevity. Additionally, poor materials can undermine even the best manufacturing processes. Here’s how to ensure material quality:
Component Sourcing Best Practices:
- Work with authorized distributors and certified suppliers
- Implement incoming quality control (IQC) procedures
- Maintain proper storage conditions for moisture-sensitive components
- Use traceability systems for component tracking
Solder Paste and Flux Quality: High-quality solder paste ensures reliable joints and reduces defects. Moreover, proper storage and handling of solder paste prevents contamination and degradation.
Mustar’s approach to material quality includes partnerships with over 200 stable global suppliers, ensuring 100% BOM compliance and cost-effective alternatives when needed.
Industry-Specific Quality Requirements
Different industries have unique quality requirements for PCBA manufacturing. Therefore, understanding these specific standards is crucial for compliance and market success.
Automotive PCBA Quality (IATF16949)
Automotive PCBAs must meet stringent reliability and safety requirements. Specifically, IATF16949 certification ensures automotive quality management systems meet industry standards.
Key Automotive Requirements:
- Zero-defect manufacturing philosophy
- Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) implementation
- Supplier quality management
Mustar has produced over 500 types of automotive PCBA, including motor driver systems and car audio electronics, all meeting IATF16949 standards.
Medical Device PCBA Standards (ISO13485)
Medical device PCBAs require exceptional quality and traceability. Furthermore, ISO13485 certification ensures medical device quality management systems meet regulatory requirements.
Medical Device Quality Requirements:
- Complete traceability from raw materials to finished products
- Risk management throughout the product lifecycle
- Design controls and validation procedures
- Sterility and biocompatibility considerations
- Regulatory compliance documentation
 Automotive PCBA meeting IATF16949 standards
Automotive PCBA meeting IATF16949 standards
Medical device PCBA compliant with ISO13485

Industrial control PCBA for harsh environments
Conclusion: Your Path to Superior PCBA Quality
Ensuring PCBA quality requires a comprehensive approach that combines proper testing methods, advanced technologies, and systematic quality management. Moreover, success depends on understanding industry-specific requirements and implementing continuous improvement practices.
The key takeaways for how to ensure PCBA quality include:
- Implementing comprehensive testing from visual inspection to advanced automated systems
- Tracking essential quality metrics like FPY and defect rates
- Building robust quality management systems with SPC and continuous improvement
- Ensuring material quality through certified suppliers and proper handling
- Meeting industry-specific standards like IATF16949 and ISO13485
Ready to Achieve Superior PCBA Quality?
Partner with Mustar for your next PCBA project and experience the difference that 25+ years of quality excellence makes. Our IATF16949 and ISO13485 certified processes, combined with advanced testing technologies and over 200 global suppliers, ensure your PCBAs meet the highest quality standards.
Contact our quality experts for a free consultation on your PCBA quality requirements.
Mustar projects:
